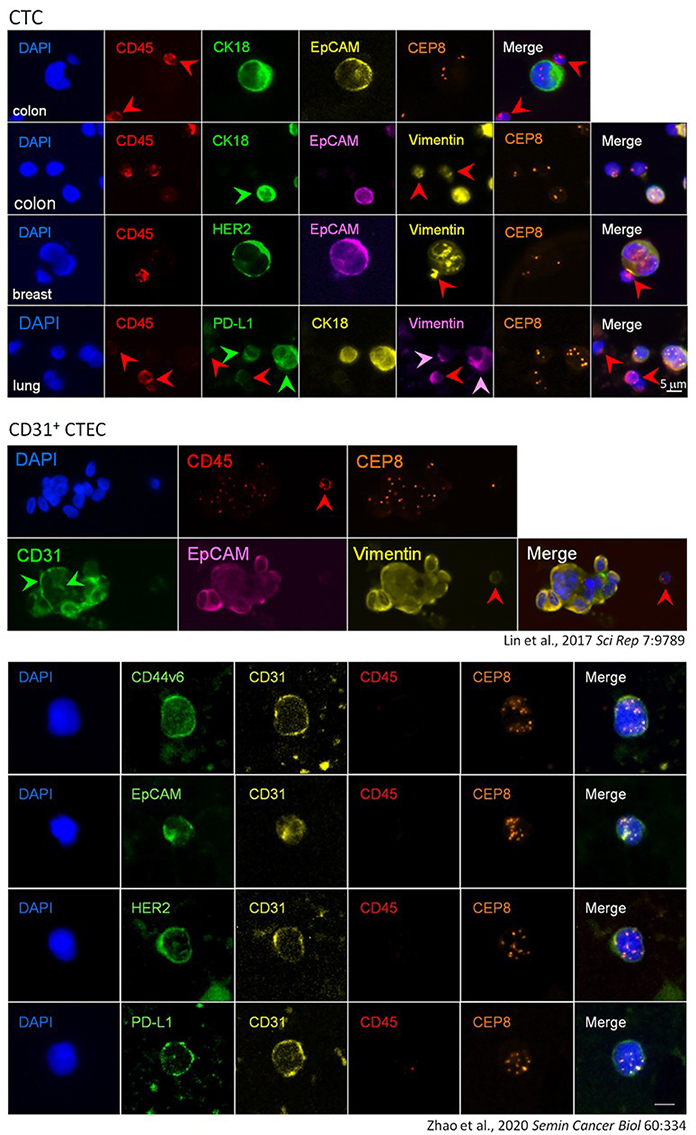
Aneuploid Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) and Circulating Tumor-derived Endothelial Cell (CTEC)
Tumor-derived endothelial cells (TECs) make up the lining of neovasculature in the tumor microenvironment (Hida and Klagsbrun, 2005 Cancer Res 65:2507). Following shedding into peripheral blood, tumor cells (TCs) and TECs turn into circulating TCs (CTCs) and circulating TECs (CTECs), respectively. TCs/CTCs and TECs/CTECs all harbor cytogenetic abnormality of aneuploid chromosomes (Lin et al., 2017 Sci Rep 7:9789). Aneuploid CTCs and CTECs, constituting a unique category of cellular circulating tumor biomarkers, have an interplay in circulation to promote tumorigenesis, neovascularization, disease progression as well as cancer metastasis. In the hypoxic tumor microenvironment, some CD31- tumor cells can be transdifferentiated into CD31+ tumor-derived endothelial cells (Lin, 2020 Cells 9:1539).

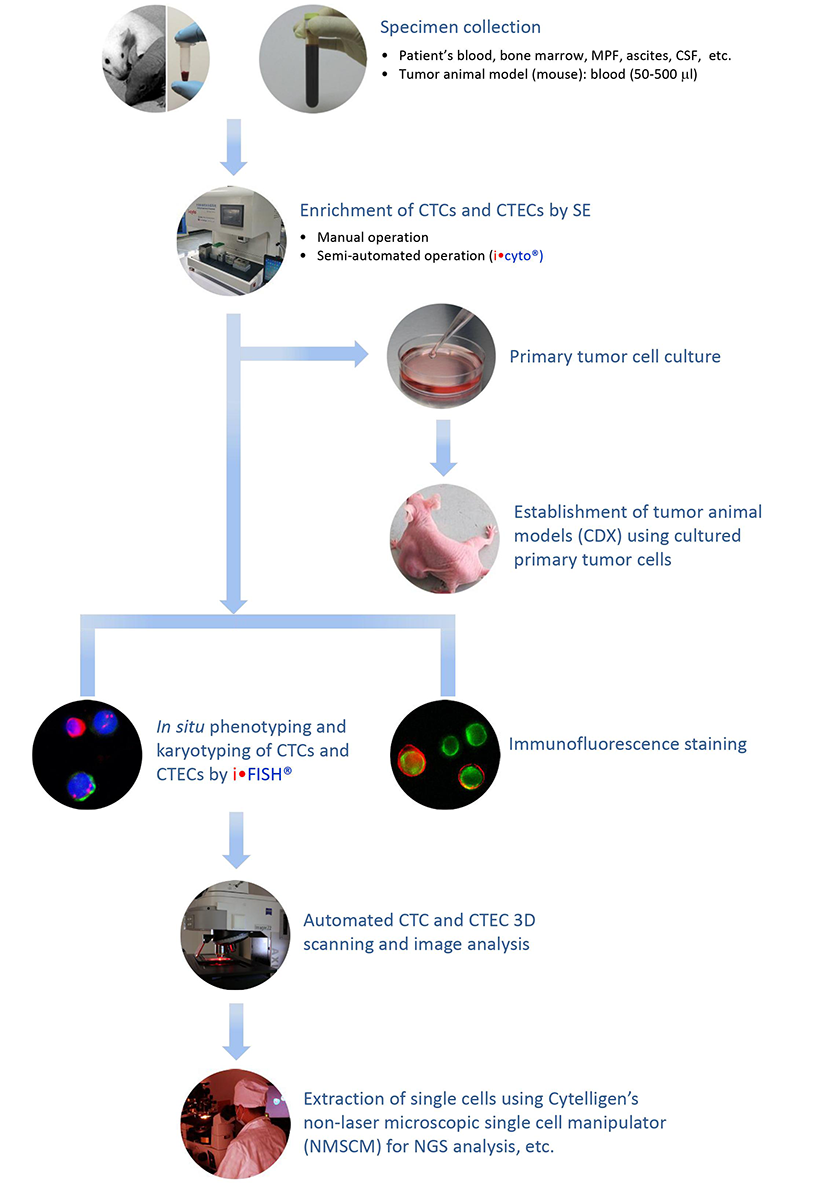
Subtraction Enrichment (SE) to Enrich Circulating Rare Cells
Principle
Non-hemolytic removal of RBCs via Cytelligen’s non-hematologic cell separation matrix
Depletion of WBCs (4-5 logs) by highly specific immuno-magnetic particles conjugated to a unique cocktail of anti-leukocytes monoclonal antibodies
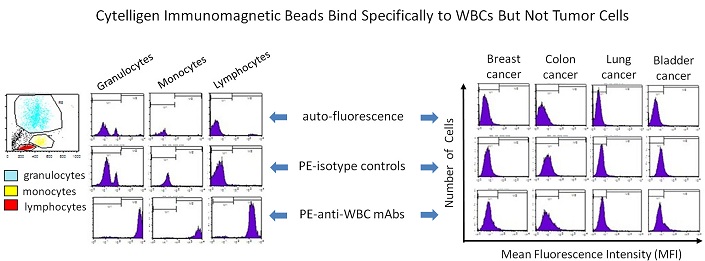
Independent of target cell surface molecules (such as EpCAM) and cell size. Enrich non-hematologic circulating rare cells including CTCs and CTECs in large or small cell size (≤ 5 μm WBCs)
Source of specimens: patients (any volume of blood, routine 6 ml) or mice (50-500 μl of blood, routine 200 μl). In addition to blood, specimens can also be collected from bone marrow, pleural effusion, ascites, cerebrospinal fluids, urine, punctured lymph node, cervical smear, etc.
Enriched, viable circulating rare cells are suitable for in vitro primary tumor cell culture and various downstream analyses
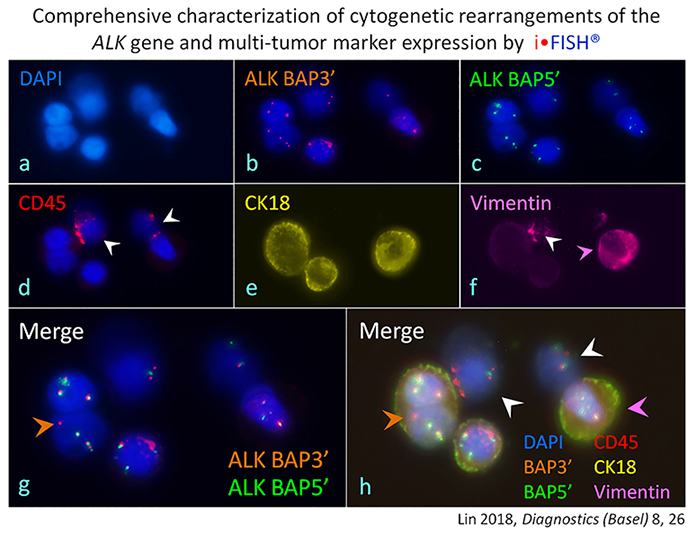
i•FISH® to Identify Diverse Subtypes of CTCs and CTECs
Principle
Cytelligen's patented technology: integrating immunostaining of multiple tumor markers and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to perform in situ phenotypic and karyotypic characterization of aneuploid CTCs and CTECs
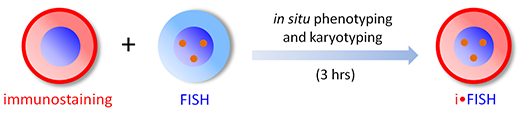
SE-i•FISH® encompasses every aspect of the cellular tri-elements including nucleic acids, protein expression and cell morphology

Time-saving
Up to six colors: available for self-selection of any tumor markers expressed on the plasma membrane, in the cytoplasm or the nucleus
i•FISH® to Comprehensively Co-detect and Characterize Diverse Subtypes of CTCs and CTECs
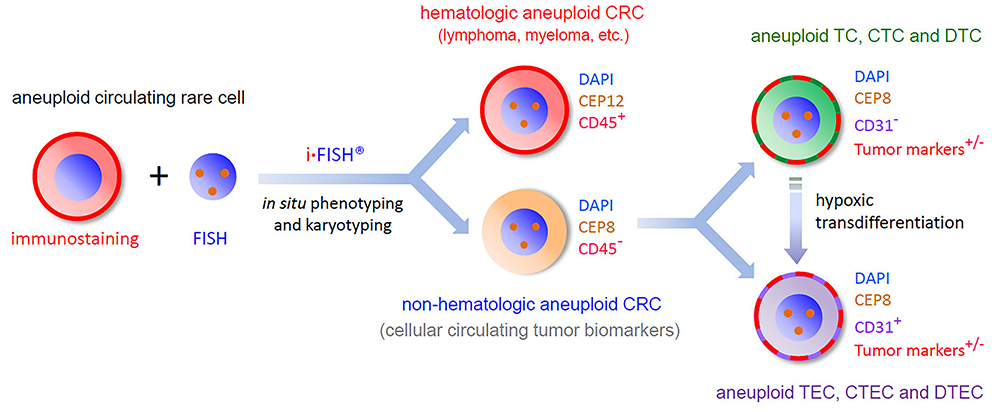
Both aneuploid CTCs and CTECs can be classified into diverse subtypes upon degree of aneuploidy, tumor marker expression and cell morphology. Each subtype possesses a distinct clinical significance, such as tumor progression, therapy resistance and cancer relapse, etc... iFISH-identified CTCs and CTECs are available for subsequent NGS-based single cell analyses.
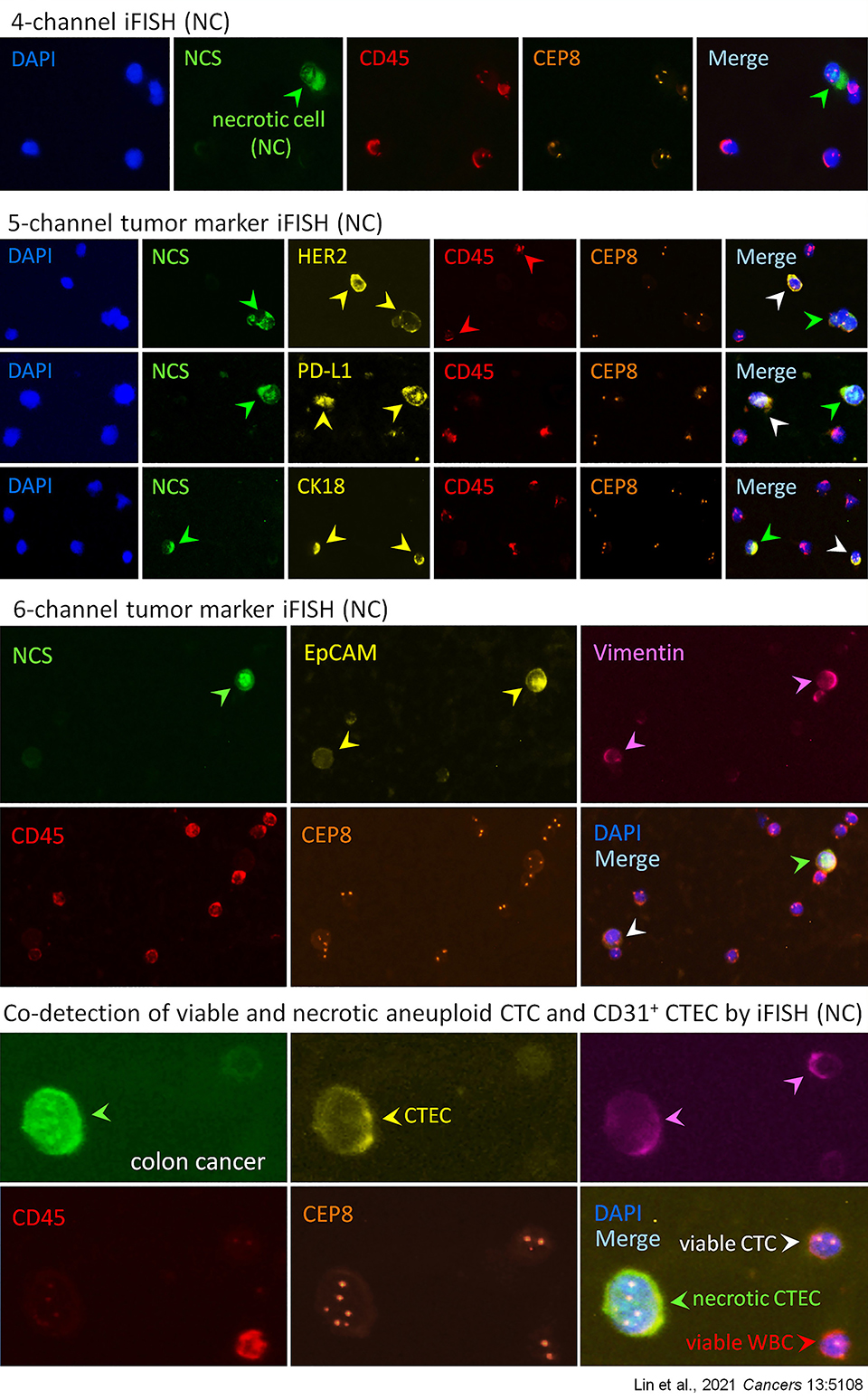
SE-i•FISH® (NC) effectively identifies and comprehensively co-detects viable and necrotic CTCs、CTECs
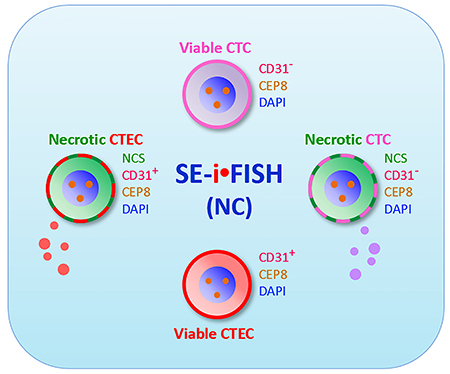
SE-i•FISH®(NC) is able to effectively enrich, detect, characterize and subcategorize various necrotic and viable CTCs and CTECs. Each subtype of CTCs and CTECs possesses distinct utility in anti-cancer drug development, translational research and clinical practice regarding risk stratification, rapid evaluation of therapeutic effects, real-time monitoring of treatment-resistance, and detection of post-therapeutic minimal residual disease (MRD).
Images of CTCs and CTECs Identified by i•FISH®
Images of Viable and Necrotic CTCs and CTECs Identified by i•FISH® (NC)
Flow Chart of SE-i•FISH®

Cytelligen, the real solutions for circulating rare cells……